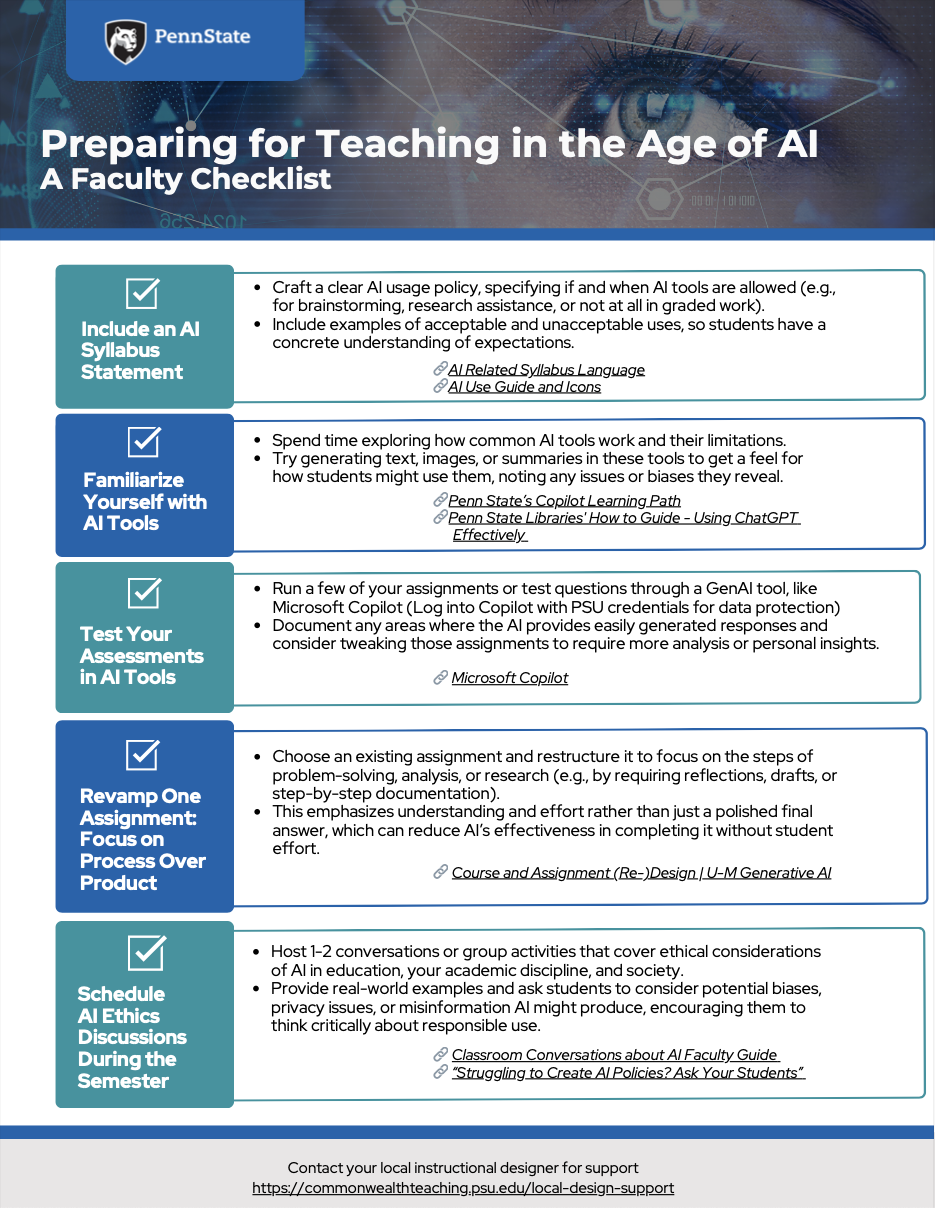
Generative Artificial Intelligence and Teaching
If you are looking for teaching support around generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), you have come to the right place. We encourage you to explore our faculty guides and other Penn State resources that are available to aid instructors in navigating teaching in the age of GenAI. If you haven’t already, take some time to play with some of the GenAI tools and begin to develop a familiarity with them. If you would like to chat with an instructional designer, please feel free to reach out and schedule a 1:1 consultation.
Coming soon!
The GenAI Use Guide for Students is a resource that was developed to facilitate conversations between faculty and students on if and when the use of GenAI tools is acceptable in assignments. Representatives from across the university are in active conversations to revise the AI Use Guide. More information will be coming in mid-summer. Stay tuned!
Faculty Guides
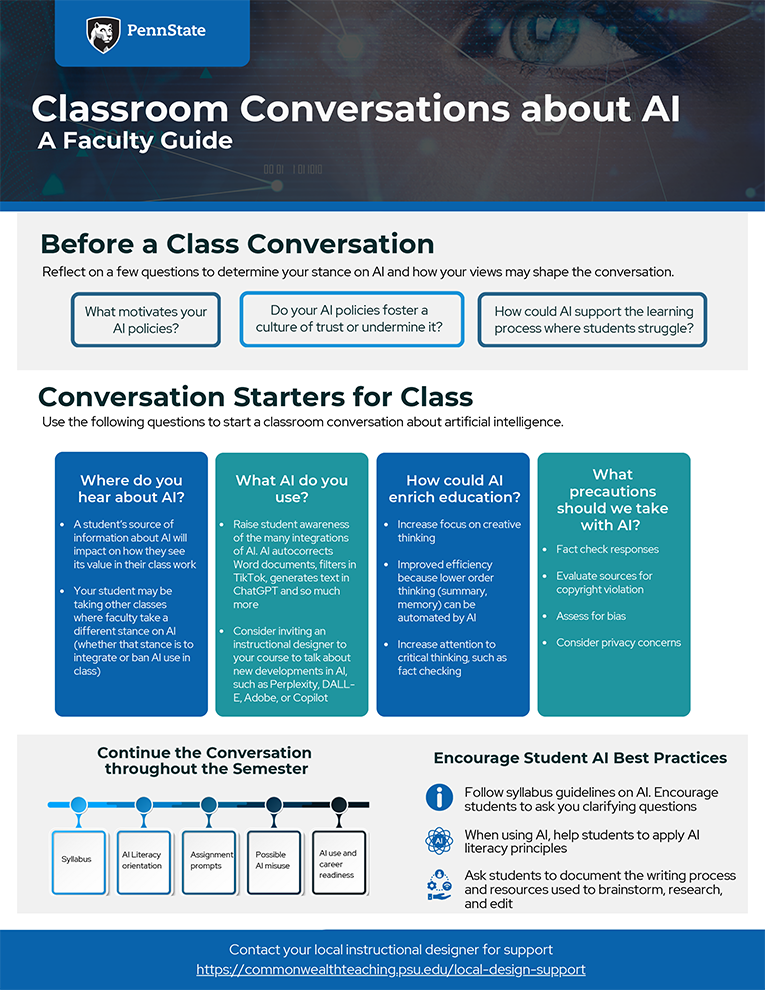
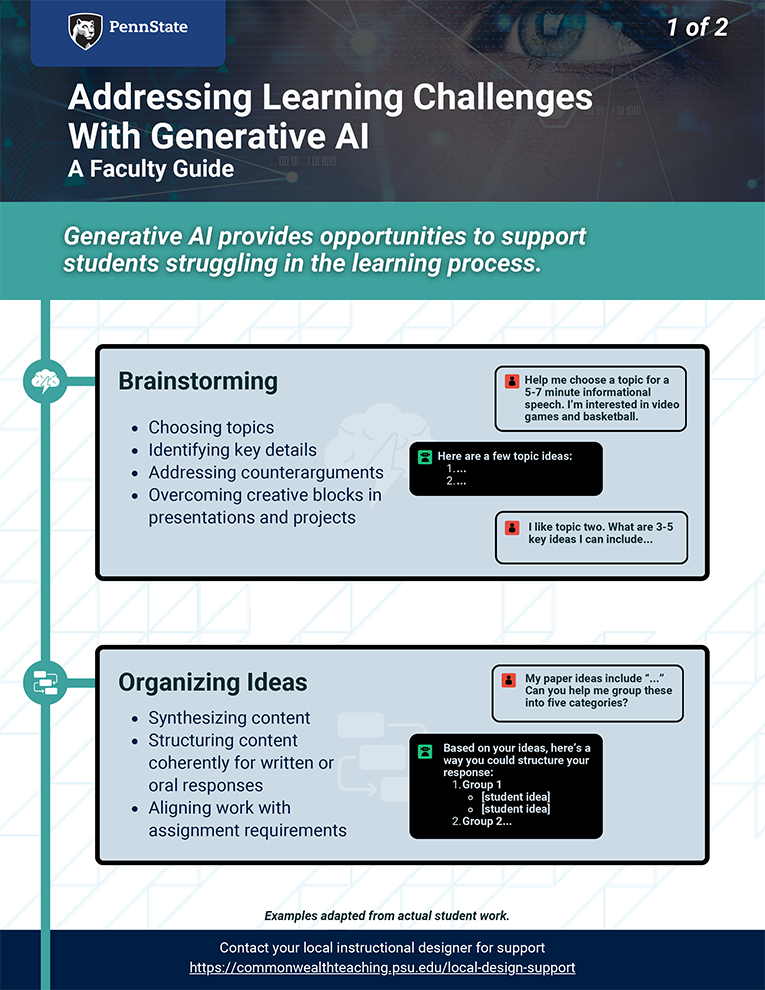
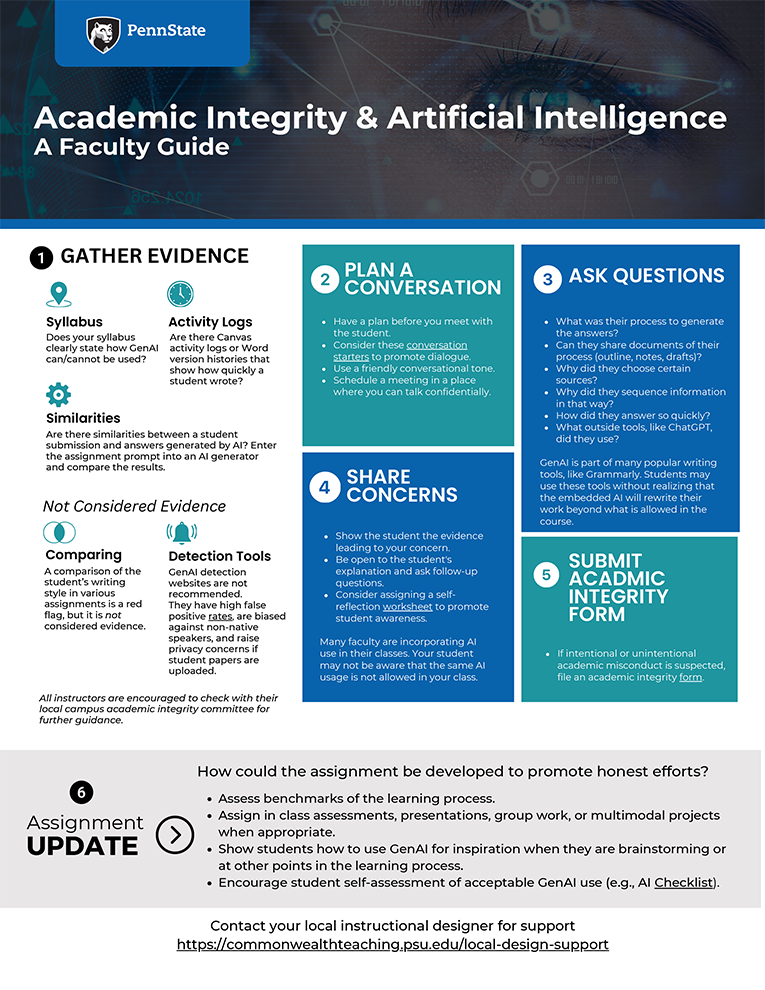
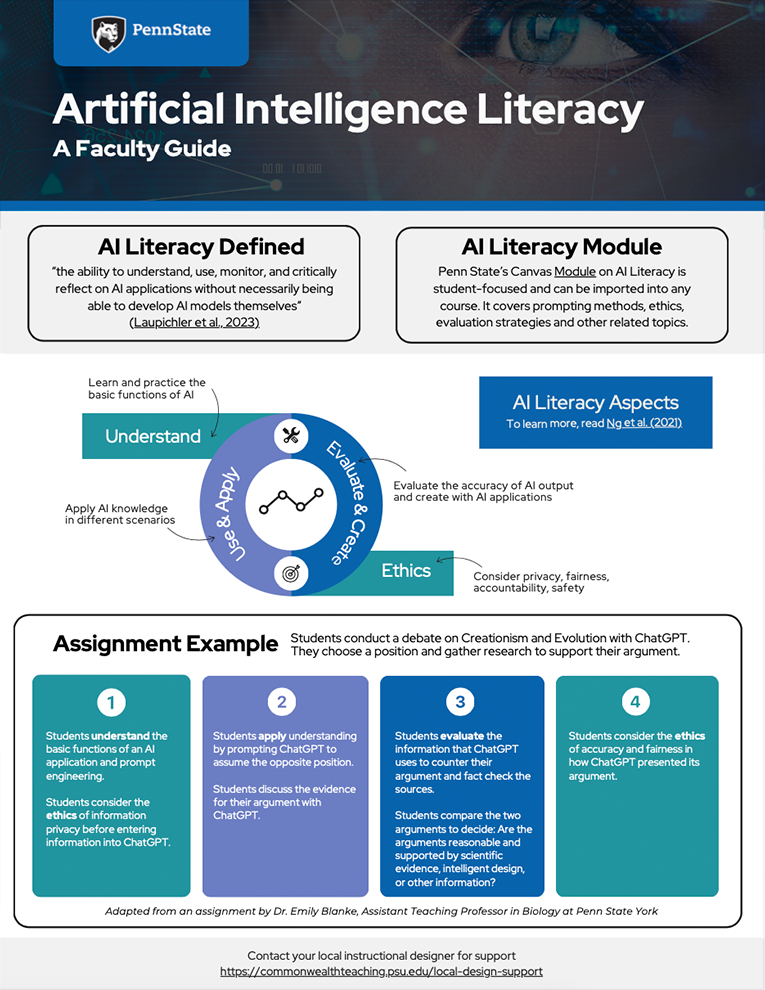
We have created several guides to support faculty in their use of GenAI in teaching and learning.
Getting Started with AI
Generative artificial intelligence is a branch of artificial intelligence that creates new content. GenAI uses techniques such as deep learning, neural networks and natural language processing to learn from existing data to generate output. Recently, several tools have been developed to allow almost any user to create GenAI output. This general availability has created benefits and challenges.
If you are getting started with artificial intelligence LLMs, such as ChatGPT, it can be helpful to experiment with these tools on your own. Penn State has access to Microsoft Copilot, which has user data protection for faculty, staff, and student accounts. You can access Copilot by visiting the Microsoft Copilot website and logging in with your Penn State credentials. Experimenting with Copilot and other GenAI tools can be helpful to you, whether you plan to teach with GenAI or not, because it can help us to see ways in which students may be using these tools.
An opening prompt to use could be:
- I teach a [describe your course – undergraduate/graduate, mode (face to face, hybrid, online), topic, title] and would like to [describe a teaching goal – include more interactive discussions, change my assessments, introduce AI]. Describe 4-5 ideas you would suggest to enhance my students’ learning.
This is just one idea for a prompt to try, and there are many resources for learning more about prompting with Generative AI. To learn more about Copilot, we recommend completing Penn State’s Copilot Learning Path (created by IT Learning & Development). And, for further exploration of prompts related to teaching and learning, we also recommend the following sites:
- AI for Education’s GenAI Chatbot Prompt Library for Educators
- University of North Florida’s open Pressbook ChatGPT in Higher Education
- University of Sydney’s AI In Education Resource Site
GenAI in Teaching: Faculty Use Cases

George Buckbee – Code Comparison Analysis
Kyle Chalupczynski – Large Language Models as a CRM Tool
Stacey Corle & Leigh Ann Haefner – ChatGPT-assisted Lesson Plan Development
Other Penn State Resources
Check out other Penn State resources on artificial intelligence.
- AI Hub – This site has several sections to explore the university’s role in advancing the science of Artificial Intelligence and its practical or theoretical bearing upon our world.
- AI and Academic Integrity – Penn State’s academic integrity website has a subsection under “Faculty Resources” on “Academic Integrity and Artificial Intelligence” that includes recommended syllabus statements and other resources.
- AI How To Guides for Students – Penn State University Libraries has created four interactive tutorials about Generative AI, how it works, and ways to use it ethically and effectively.
- Generative AI: ChatGPT and Beyond – This LibGuide from Penn State University Libraries explains what LLMs are, links to interesting reads, and more details about some of the more widely used LLMs (like ChatGPT, Gemini, Elicit, etc.).
Updated: December 7, 2024